Procedures and Surgeries for Managing Heart Failure: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Heart Failure
Heart failure is a critical medical condition characterized by the heart’s inability to pump blood efficiently throughout the body. While heart failure is not curable, numerous treatment options are available to manage its symptoms and improve the quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
This chronic condition can result from various underlying factors, such as coronary artery disease, hypertension, or cardiomyopathy. Symptoms of heart failure may include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs and abdomen, and difficulty performing daily activities.
Despite its challenges, early diagnosis and appropriate management can significantly improve outcomes and enhance the overall well-being of patients living with heart failure. By working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals can develop personalized treatment plans that may include medication, lifestyle modifications, and, in some cases, surgical interventions to manage their condition and improve their quality of life effectively.
Coronary Stents for Heart
In cases where heart failure occurs due to restricted blood flow to the heart caused by narrowed coronary arteries, a procedure called coronary stenting may be recommended. During this minimally invasive procedure, a coronary stent is inserted into the narrowed artery during a cardiac catheterization. The stent widens the artery, restoring proper blood flow to the heart muscle. This alleviates the restriction and improves overall cardiac function, thereby helping to manage symptoms of heart failure and enhance the patient’s quality of life. Coronary stenting is a common and effective intervention used to address coronary artery disease and its associated complications, offering patients a less invasive alternative to traditional open-heart surgery.
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG), commonly called coronary bypass surgery, is a surgical procedure to restore blood flow to the heart muscle when the coronary arteries are severely blocked or narrowed. This condition, known as coronary artery disease (CAD), occurs when plaque buildup or atherosclerosis restricts blood flow to the heart, leading to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and increased risk of heart attack.
During CABG surgery, the surgeon creates new pathways for blood flow to bypass the blocked or narrowed segments of the coronary arteries. This is achieved by harvesting healthy blood vessels, typically from the patient’s leg (saphenous vein) or chest (internal mammary artery), grafting them onto the coronary arteries beyond the blockages. These newly grafted vessels serve as alternate routes for blood to reach the heart muscle, effectively restoring adequate blood supply and oxygen delivery.
CABG surgery is typically recommended when coronary artery blockages are too severe to be effectively treated with other interventions, such as coronary stenting. It may also be indicated in cases where multiple coronary arteries are affected or when the left main coronary artery, a critical artery supplying a large portion of the heart, is significantly narrowed.
The procedure can be performed using either traditional open-heart surgery or minimally invasive techniques, depending on the patient’s condition and the complexity of the surgery. In conventional CABG surgery, the surgeon makes an incision in the chest and temporarily stops the heart using a heart-lung bypass machine while grafts are attached. In minimally invasive CABG, smaller incisions are made, and the heart may continue beating during the procedure, reducing recovery time and potential complications.
Following CABG surgery, patients typically require a period of hospitalization for monitoring and recovery. They may also participate in cardiac rehabilitation programs to help improve cardiovascular health and regain strength. With proper care and lifestyle modifications, most patients experience significant improvement in symptoms and quality of life after CABG surgery, reducing the risk of future heart-related complications.
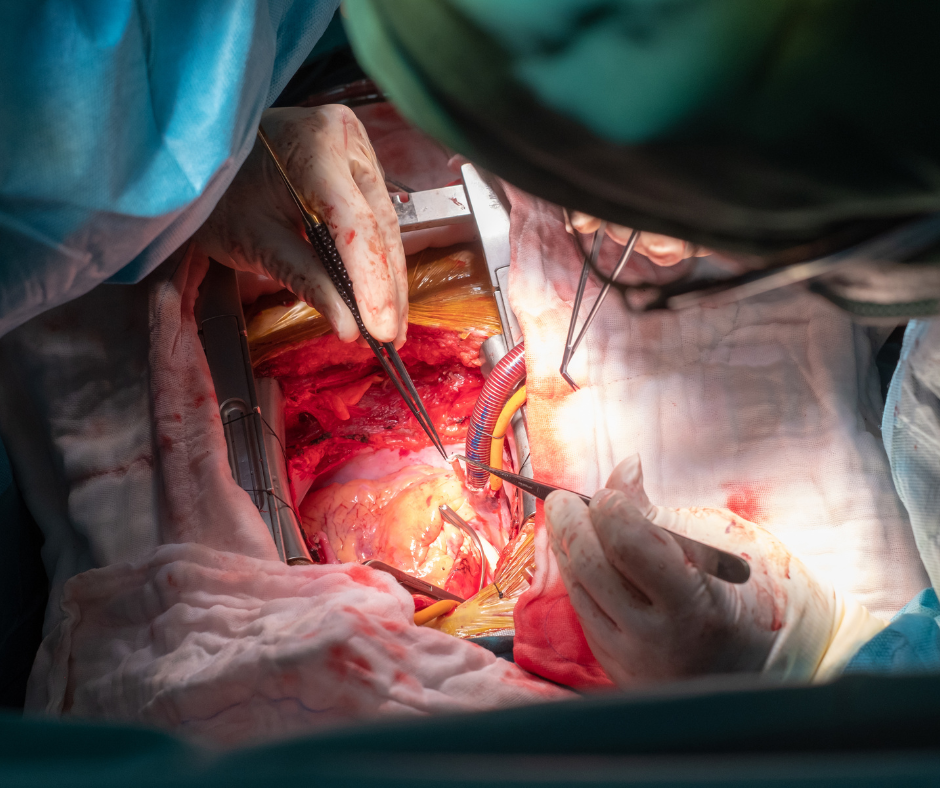
How Does CABG Work?
In this open-heart surgery, blood vessels from the leg, arm, or chest are harvested and implanted near the blockage site. This bypass allows blood to flow freely to the heart, mitigating the effects of heart failure.
Heart Valve Surgery
Heart valve surgery is performed to repair or replace damaged or malfunctioning heart valves. Heart valves play a crucial role in regulating blood flow within the heart by ensuring that blood flows in the correct direction. When heart valves become diseased or damaged, they may not function properly, leading to shortness of breath, chest pain, fatigue, and swelling in the legs and abdomen.
There are several types of heart valve surgery, including:
Valve Repair: During valve repair surgery, the surgeon may reshape, tighten, or reconstruct the damaged valve to improve its function. This approach is often preferred when possible, as it preserves the natural anatomy of the heart and may provide better long-term outcomes.
Valve Replacement: In cases where valve repair is not feasible or practical, valve replacement surgery may be necessary. During this procedure, the damaged valve is removed and replaced with either a mechanical valve made of durable materials or a biological valve derived from human or animal tissue. The choice of valve replacement depends on various factors, including the patient’s age, medical history, and lifestyle.
Heart valve surgery may be performed using either traditional open-heart surgery or minimally invasive techniques, depending on the patient’s condition and the complexity of the procedure.
Minimally invasive approaches involve smaller incisions and may result in faster recovery times and fewer complications than open-heart surgery.
After heart valve surgery, patients typically require a period of recovery and rehabilitation to regain strength and resume normal activities. Following surgery, patients will also require lifelong monitoring and may need to take medications to prevent blood clots or manage other heart-related conditions.
Overall, heart valve surgery is a critical intervention for individuals with heart valve disease, aiming to restore proper heart function, alleviate symptoms, and improve overall quality of life.
Faulty heart valves can also contribute to heart failure. In such cases, heart valve surgery may be advised.
Repair or Replacement?
The faulty valve may be repaired or replaced with an artificial one, depending on its condition.
Managing Heart Failure: The Bottom Line
While there is no definitive cure for heart failure, available treatments aim to manage symptoms and improve the patient’s quality of life.
Conclusion
Understanding the surgical options and medical procedures for heart failure can empower patients and caregivers to make informed decisions. Always consult your cardiologist for a diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your needs.
Could you contact a heart specialist near you?
The above external link is for the American Heart Association’s webpage on treatment options for heart failure: American Heart Association – Treatment Options for Heart Failure.
Meet Your Cardiologist
Contact us today to take control of your heart health journey. Our expert team is here to provide personalized guidance and support.